|
This is a comprehensive predictive test available for assessing the risk of toxicity due to 5-FU based chemotherapy. It detects genetic variants in one gene, DPYD (dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase), that is responsible for a significant portion of serious adverse reactions to 5-FU-based therapy.
List of 5-FU based drugs: Xeloda®, Adrucil®, Efudix®, Carac®, Fluoroblastin®
Xeloda® is the first FDA-approved oral chemotherapy used for treatment of metastatic breast and colorectal cancer. Xeloda® is the inactive form (prodrug) of 5-FU and gets converted to its active form by a naturally occurring enzyme called thymidine phosphorylase, which is highly expressed in tumor cells.
Click here for more safety information on Xeloda®.
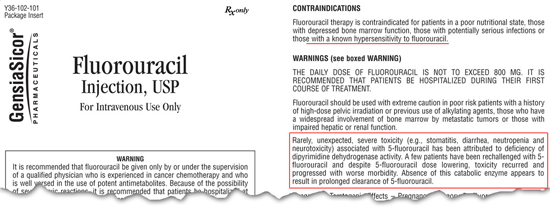
FDA label warning. Recent studies have identified a genetic variation in DPYD that correlates with an increased risk of flouorouracil therapy-associated Grade 3-4 toxicity. About 1 in 14 (7%) patients treated with 5-FU develop a Grade 3-4 toxicity (neutropenia, nausea or vomiting, severe diarrhea, and neuropathy). Therefore, the US Food and Drug Administration has revised the labeling requirement for 5-FU based drugs to contain a warning for hypersensitivity in some individuals.
Functional role of DPD. Active metabolites of 5-FU inhibit production of thymidine, an essential component of DNA. Thymidine deficiency in proliferating cells (ie. cancer cells) results in inhibition of DNA synthesis and leads to cell death.
Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) is the rate limiting enzyme in catabolism of thymidine and uracil.1 It is also the enzyme responsible for degradation and elimination of >80% of 5-FU.2 Genetic variants that reduce the activity of DPD lead to decreased 5-FU catabolism, resulting in a significant increase in the effective 5-FU dose in the body. Clinical studies have shown that individuals with this polymorphism have a 7-fold increased risk of Grade 3 or 4 toxicity during 5-FU therapy.3
Reporting. This procedure tests for a guanine to adenine point mutation at the 5’-splice site of DPYD (IVS14+1G>A).
| DPYD IVS14+1G>A mutation detected |
| No mutation detected |
Interpretation. Individuals in the HIGH RISK group may have up to 7-fold increased risk of developing Grade 3 or 4 5-FU-associated toxicity.
Intended Use
EntroGen’s DPYD Genotyping Kit is provided for research use only (RUO). Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
References
- Lu et al., Cancer Res. 1993 Nov 15;53(22):5433-8.
- Sulzyc-Bielicka et al., Pharmacol Rep. 2008;60(2):238-42
- Raida et al., Clin Cancer Res, 2001; 7:2832–2839
|

|
Product Overview
» Detects the most common DPYD*2A variant
» Can be preformed under 2 hours
» Simple setup and interpretation
Click here to request more information about this product.
|